Ideation Meaning and Process
Ideation is the creative process from which ideas are generated, developed and communicated, all the way to being implemented. Through techniques like brainstorming, mind mapping, and SCAMPER, participants explore various possibilities and connections to solve challenges and gain new insights.
What is Ideation?
Ideation is a space where creativity and innovation meet. It's a collaborative environment where open innovation and co-creation are encouraged. By working together as a team, participants can build on each other's ideas, combining different knowledge to create unique solutions. Prototyping and testing ensure that the most promising ideas are refined and implemented. Innovation management platforms contribute to efficiency and organization in executing the process.
Throughout the journey, perseverance and growth are encouraged. Successes are celebrated, and any setbacks are seen as opportunities for learning and improvement in future ideation sessions.
In this stimulating world of ideation, the seeds of progress are sown, propelling individuals and organizations towards brighter and more impactful futures. It's a process that promotes continuous improvement, drives innovation and positive change across various fields.
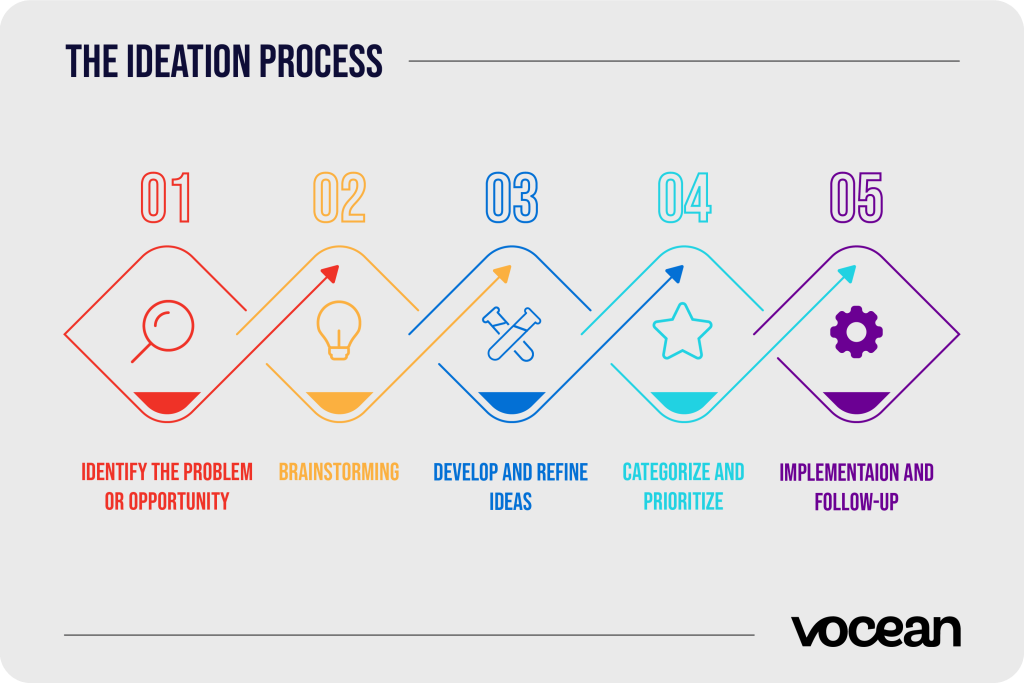
The Ideation Process
Ideation is not a single action but a whole process from generation to implementation. For successful ideation, each step is important and they will be explained here:
Identify the Problem or Opportunity
Clearly define the challenge you want to tackle or the opportunity you want to explore.
Brainstorming
Generate as many ideas as possible. Encouraging completely judgment-free creativity allows participants to dare share their wildest ideas, which is often where the most genius innovations arise. Albert Einstein's quote on innovation supports this view: 'If an idea doesn't seem absurd at first, there's no hope for it.'
Develop and Refine Ideas
Work on the selected ideas, develop them and refine them together to make them more feasible and effective.
Categorize and Prioritize
Organize and categorize the ideas, then prioritize the most promising ones based on relevance and potential impact.
Implementation and Follow-up
Implement the chosen ideas and regularly evaluate the results.
Why is Ideation Important?
Ideation is a powerful process with many benefits. It enables multiple perspectives and encourages innovation. It also promotes creativity, which can lead to unusual ideas that wouldn't have been thought of otherwise. By generating and evaluating multiple solutions, the organization's problem-solving ability improves. Ideation enables continuous improvement and empowers employees, promoting a positive work culture. In summary, it drives positive change and growth within organizations. Here are 5 key benefits of ideation explained in more detail:
Diverse Perspectives
Creativity and Innovation
Effective Problem-solving
Continuous Improvement
Employee Engagement
How to Succeed with Ideation
We know there are many benefits to conducting ideation processes, but the results don't come by themselves. Here are some tips on how to succeed with ideation:
Create a Non-judgmental and Diverse Environment
Set Clear Goals and Constraints
Use Creative Ideation Techniques
Encourage Collaboration and Teamwork
Combine Ideas
Test the Ideas
Document and Organize Ideas
Iterate, Celebrate Success, and Learn from Failures
Use an Ideation Tool
Challenges of Ideation
It's clear that ideation brings many benefits, but there are some challenges to be aware of. We've compiled a list of 5 key challenges and some tips on how to overcome them:
Evaluation and Selection of Ideas
Overcoming the Fear of Being Judged
Generating Valuable Ideas
Implementation and Alignment with Organizational Goals
Managing the Process
Ideation Tools and Techniques
There are several proven techniques that can be used to stimulate creative thinking and generate new ideas.
Brainstorming
Reverse Thinking
SCAMPER
Forced Relationship
The 5 W's
The 5 W's stands for a set of questions to ask. By asking these questions, you get a better picture of the problem at hand. The five different types of questions can be used in different ways depending on what you want to achieve. For example, the questions can be used both to understand a problem or to improve an already existing potential solution. The 5 W's are: What, Why, Who, When, Where. Another variant is 5 'whys'. This method is used to get a deeper understanding of a problem. By continuing to ask 'why?' you go from a thorough understanding down to the roots of the problem.
Tip: If you want a more constructive and solution-oriented approach instead of just trying to find answers to the question 'Why?', try instead asking 'How?'.
Mind Mapping
Brainwriting
Storyboarding
Six Thinking Hats
Conclusion
Ideation is a powerful process that promotes creativity, problem-solving, and innovation, and is an important part of growth within organizations. By using different techniques and tools, participants can explore a wealth of opportunities to overcome challenges and innovate. The open and supportive environment where diversity and collaboration are embraced helps open up new perspectives and possibilities. With the right techniques, tools, and mindset, organizations can harness the power of ideation to drive innovation and positive change.
It's clear how important a platform for ideation is to successfully come up with new ideas and overcome challenges. Vocean enables effective inclusion of people in ideation processes and makes it easy to handle large amounts of data, thus helping to find breakthrough solutions.
Ready to Start Your Ideation?
Discover how Vocean can help you effectively involve people in your processes and find breakthrough innovations.